Key Takeaways:
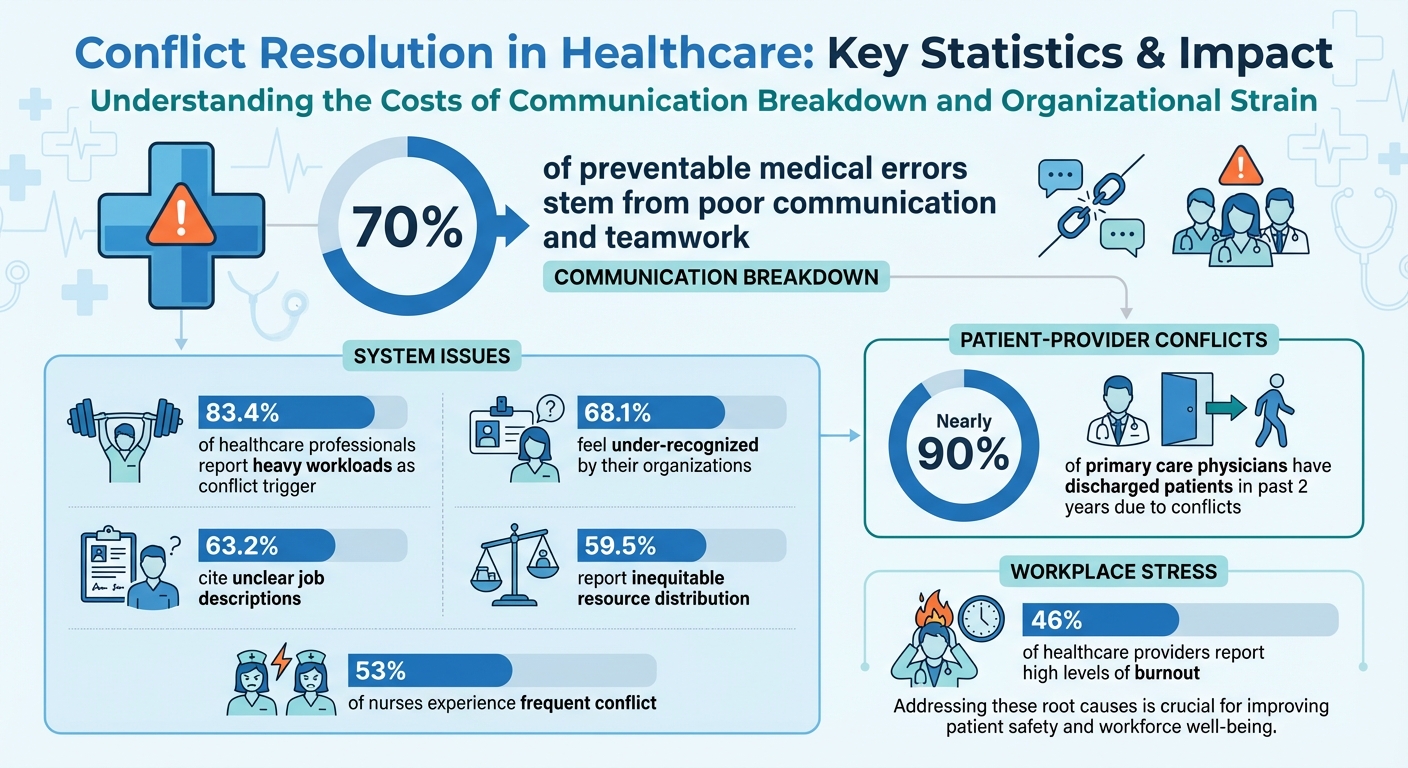
- Impact on Patient Outcomes: 70% of preventable medical errors stem from poor communication and teamwork.
- Common Conflict Sources:
- Team disputes: personality clashes, role ambiguity, and interdisciplinary disagreements.
- Patient-provider issues: miscommunication, differing expectations, and personal beliefs.
- System-level problems: heavy workloads, unclear job roles, and resource allocation.
- Resolution Techniques:
- Active listening and respectful communication.
- Managing emotions and setting boundaries.
- Collaborative problem-solving and compromise.
- Training Opportunities: Workshops, role-playing, and online courses like TeamSTEPPS help healthcare professionals build conflict management skills.
Addressing conflicts early and constructively not only reduces risks but also strengthens team dynamics and improves patient safety.
Healthcare Conflict Statistics: Impact on Teams and Patient Safety
Conflict Management Through Communication in Healthcare
sbb-itb-7a67ffa
Common Types of Conflicts in Healthcare Settings
Conflicts in healthcare often stem from interpersonal issues, professional differences, and unclear roles. Recognizing these early can help prevent escalation.
Team Member Disagreements
Conflicts within teams can arise in several ways:
- Interpersonal disputes: These often result from personality clashes, low emotional intelligence, or competing personal goals.
- Interdisciplinary disagreements: Tensions between professions, such as physicians and nurses, may escalate in high-pressure situations like hospital admissions. Factors like professional identity and hierarchical dynamics contribute to these conflicts.
- Role ambiguity: When roles are unclear or support is lacking, disagreements are more likely. Leadership style also plays a role – laissez-faire leaders may allow blame cultures to develop, while authoritarian approaches can damage trust.
Communication breakdowns within teams are another frequent cause of conflict, and these issues extend to patient-provider interactions as well.
Patient-Provider Disputes
Conflicts between patients and providers often stem from poor communication. Misunderstandings can arise from using overly complex medical jargon, weak non-verbal cues, or differing expectations about treatment plans. For instance, nearly 90% of primary care physicians have discharged patients in the past two years due to issues like disruptive behavior, violations of controlled substance policies, or chronic non-payment.
"It is more accurate to regard conflict as the result of a difficult relationship between the patient and the physician."
– ACOG Committee on Ethics
Other factors include differences in personal or religious beliefs, a provider’s conscientious refusal to offer specific treatments, or a patient’s history of trauma. Providers with lower emotional intelligence may also face more frequent conflicts.
Organizational and System-Level Problems
Systemic issues within healthcare organizations are a major source of conflict. In the U.S., 83.4% of healthcare professionals report heavy workloads as a significant trigger, while 68.1% feel under-recognized by their organizations. Among nurses, 53% experience frequent conflict.
Other structural challenges include unclear job descriptions (reported by 63.2% of staff) and inequitable resource distribution (cited by 59.5%). Additional factors, such as steep power gradients, overextended managers, and limited staff input in decision-making, further strain workplace dynamics. Even physical space and the demands of shift work can escalate tensions.
"Organizations identify and take action to prevent/mitigate factors contributing to conflict, for example: effects of shift work; team composition and size; workload and staffing; manager span of control; level of staff involvement in decision-making… resource allocation; diversity in the workplace; and physical space."
– Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario
These systemic issues often simmer beneath the surface before erupting into open conflict. Regular assessments, incident reporting, and staff surveys are critical for identifying and addressing these problems early. A thorough understanding of these conflict types is key to developing effective resolution strategies and improving workplace harmony.
Practical Techniques for Resolving Conflicts
To effectively resolve conflict, start by identifying the type of disagreement and then choose the best approach to address it. These strategies not only help resolve issues but also build stronger teamwork and improve outcomes, especially in patient care settings.
Active Listening and Understanding Others
Active listening means giving your full attention to the speaker. This involves maintaining eye contact, nodding, and offering brief verbal cues like "I see" or "I understand." The goal is to genuinely comprehend the other person’s perspective before responding.
"How can I truly understand the other person’s perspective?" – Stephen Covey
A useful method is paraphrasing – repeating back the person’s concerns in your own words. This shows you’ve understood their point and reassures them that they’ve been heard. Avoid jumping to conclusions or responding too quickly; sometimes, silence can encourage deeper understanding.
Once you’ve fully grasped their perspective, communicate your own views respectfully and clearly, ensuring your tone and words reflect mutual respect.
Respectful Communication Methods
The way you express your concerns can significantly impact how they’re received. Assertive communication allows you to be honest about your thoughts and feelings while respecting others. Using "I" statements, such as "I feel that…" or "I noticed…", helps you express your viewpoint without sounding accusatory.
Disarming statements can also defuse tension before disagreements escalate. For example, saying, "I see why this is important to you, and I’d like to share my perspective", can help reduce defensiveness. Dr. M. Kaufmann offers a great example:
"Interesting – it seems we have different points of view. Do you mind if I explain where I’m coming from?"
Bringing the focus back to shared goals, like ensuring patient safety or delivering quality care, reminds everyone that despite differences, the team is working toward the same outcome.
Calming Tense Situations
Managing emotions early is key to preventing conflicts from spiraling. Pay attention to warning signs like raised voices, stiff posture, or avoidance of eye contact. If you notice these, stay composed by taking slow, deep breaths and speaking in a calm, measured tone.
When emotions run high, a time-out can be invaluable. Agree to pause the discussion and revisit it later in a private setting after everyone has had time to cool down. Before resuming, ask each person to write down their understanding of the issue and share it aloud. This ensures everyone is on the same page.
Body language also plays a significant role. Keep your posture open – avoid crossing your arms, pointing fingers, or standing too close. A neutral facial expression and clarifying questions can signal that you’re listening. If behavior becomes inappropriate or threatening, calmly set boundaries. For example, you could say, "This behavior is not acceptable, and if it continues, there will be consequences." If the situation escalates toward violence, prioritize safety by removing yourself and contacting security immediately.
Different conflicts require different solutions. Collaborative problem-solving works well for fostering long-term team harmony, as it incorporates all viewpoints to find a mutually beneficial solution. When time is limited, compromise can provide a faster resolution, with both sides making concessions. The key is to address conflicts early, preventing them from growing into larger problems.
Training Programs and Resources
Mastering conflict resolution takes more than just theory – it demands hands-on practice and structured learning. For healthcare professionals, the best training mirrors the real-life challenges they face daily.
Interactive Workshops and Practice Scenarios
The most impactful training methods go beyond traditional lectures and embrace experiential learning. By using simulations, role-playing, and small group exercises, participants can safely practice de-escalation and negotiation techniques. One standout example is TeamSTEPPS 3.0, an evidence-based framework designed to enhance communication and teamwork in healthcare. It offers tools specifically aimed at resolving conflicts within multidisciplinary teams and provides both 8-week virtual master training courses and 2-day in-person sessions.
Interactive workshops also encourage participants to create actionable strategies they can use right away. Nicole Wingfield, RN Clinic Director at So Others Might Eat (SOME), shared her experience:
"This course has made me more aware of my weaknesses and strengths as a leader. Most importantly, I’ve learned that leadership is something that will always need cultivating".
These types of exercises foster self-awareness, helping participants identify their personal conflict styles and emotional triggers. This awareness is key to preventing tensions from escalating in the workplace. By pairing these workshops with ongoing career development opportunities, healthcare professionals can reinforce and expand their conflict resolution skills.
Adding Conflict Resolution to Career Development
Incorporating conflict resolution training into long-term career development benefits not just individual skills but also team collaboration and patient care. Flexible program formats make it easier to fit this training into busy clinical schedules. Options range from quick 20-minute micro-modules (offering 0.25 CME credits) to more in-depth, self-paced certificates that span several months. For example, the AAPL Resolving Conflict course provides 7 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits and is priced at $742.00 for non-members.
For those just starting their healthcare careers, building these skills early can be invaluable. Platforms like HealthCareer Certs offer fully online certification programs for roles such as Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA) and Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT). These programs combine self-paced learning with one-on-one instructor guidance, focusing on clinical skills while fostering strong communication abilities – an essential foundation for effective teamwork.
As careers progress, specialized conflict resolution training, such as graduate certificates, weekend cohort programs, or professional development courses, can help healthcare professionals stay prepared to handle the interpersonal complexities of patient care and team management.
Practical Examples and Proven Methods
Real-life scenarios provide a clear picture of how conflict resolution techniques and training programs can lead to effective outcomes, especially in high-pressure environments like healthcare.
Examples of Resolved Conflicts
Healthcare settings often face conflicts that require structured and proactive intervention. Take, for example, two nurses disagreeing during a shift handover about the quality of wound dressing or a physician speaking disrespectfully to a nurse in front of a patient. In these cases, a neutral mediator, such as a nurse leader, can step in to facilitate a clear, solution-driven conversation. Resolving these issues typically involves private, assertive discussions where boundaries are respectfully communicated. As Brian Gallagher, Physician Assistant at Tribal Health, points out:
"We put patient care and patient safety first".
The nature of the conflict often dictates the resolution approach. Task-based conflicts – such as differing opinions on the best method to bandage a wound – might require a collaborative review of clinical evidence. On the other hand, value-based conflicts, stemming from personal beliefs or differing perspectives, demand a more sensitive strategy. These situations require acknowledging individual viewpoints while keeping the shared goal of patient safety front and center.
When emotions run high, the "24-Hour Rule" can be invaluable. This approach allows a cooling-off period before revisiting the issue in a neutral setting. Dianne Kandt, RN and Nurse Supervisor, advises:
"Always remain kind. Everyone deserves a grace note. Assume the best. Don’t be afraid to address specific behaviors. Praise in public, criticize in private, and be ready to forgive".
Such strategies not only resolve immediate disputes but also strengthen team dynamics over time.
Building a Teamwork-Focused Environment
Resolving conflicts is important, but creating a culture that minimizes them is even better. A teamwork-focused environment starts with fostering psychological safety. This means encouraging team members to ask questions, seek feedback, and voice concerns without fear of judgment or backlash. With nearly half (46%) of healthcare providers reporting high levels of burnout, prioritizing this kind of supportive atmosphere is essential.
Organizations can take several steps to prevent conflicts from arising. Establishing clear reporting structures – such as escalating concerns through a chain of command (Charge Nurse > Unit Manager > Director of Nursing > Compliance Officer) – ensures that everyone knows where to turn for support. Tools like SBAR (Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation) also play a key role, helping ensure that patient information is communicated clearly and effectively, reducing task-based misunderstandings.
Role clarity is another critical factor. When team members understand their responsibilities and scope of practice, it reduces ambiguity and friction. Moving away from rigid hierarchies toward shared leadership models fosters open communication and trust, empowering everyone to contribute to patient care decisions, regardless of their role.
Physical proximity and informal interactions also matter. Colocating team members and encouraging casual conversations can help build stronger relationships, preventing minor issues from escalating. Regular, structured meetings focused on patient care and team operations ensure that all voices are heard and decisions are made collaboratively. These practices, combined with thorough onboarding for new team members, create an environment where conflicts are addressed early and constructively. The ultimate goal? Keeping the focus firmly on patient safety and delivering quality care.
Conclusion
Managing conflict effectively can turn disagreements into chances for team improvement and safer patient outcomes. When addressed properly, conflicts not only strengthen team dynamics but also enhance critical thinking and, most importantly, patient safety. As the Canadian Medical Protective Association highlights:
"Addressing conflict within a team is key to promoting the safety of medical care and achieving a workplace culture that values respect and collegiality".
On the other hand, unresolved conflicts can lead to serious issues like avoided discussions, risky workarounds, and communication breakdowns – all of which can compromise patient safety. Effective conflict resolution, however, fosters an atmosphere of psychological safety. This means creating a space where team members feel confident to voice concerns, ask questions, and challenge ideas without fear of being judged.
Given these risks, mastering conflict resolution techniques is more than helpful – it’s necessary. Approaches like active listening, using disarming statements, holding structured meetings, and establishing clear escalation pathways offer practical ways to de-escalate tension and promote collaboration. StatPearls emphasizes this point:
"Conflict can, in fact, be positive when managed properly. Conflict can foster team-building, critical thinking, new ideas, and alternative resolutions".
Beyond these techniques, continuous training reinforces these skills, minimizing risks and enhancing care quality. Many organizations now recognize conflict management as a critical leadership skill. Developing these abilities not only reduces medico-legal risks but also improves team cohesion, positioning you as a leader who prioritizes patient care while navigating interpersonal challenges effectively.
For healthcare professionals, building conflict resolution skills is essential to maintaining high standards of patient care. Whether you’re new to the field or advancing in your career, these skills will remain invaluable for years to come. Mastering them is key to creating a workplace culture rooted in safety, respect, and collaboration.
FAQs
How does poor communication contribute to medical errors in healthcare?
Poor communication in healthcare can have severe consequences, leading to medical errors when critical information is misunderstood, ignored, or misinterpreted. For instance, unclear instructions about medications or treatment plans might result in incorrect dosages, harmful drug interactions, or delays in care. Likewise, a breakdown in communication between healthcare professionals, like physicians and nurses, can lead to diagnostic mistakes or inappropriate treatments, putting patient safety at risk.
The effects of poor communication extend beyond isolated errors. It can damage trust, lower patient satisfaction, and create an environment where mistakes are more likely to happen. To address this, healthcare teams must adopt effective communication practices, such as team huddles, well-defined escalation protocols, and structured care plans. Prioritizing clear, respectful, and thorough communication is essential for ensuring patient safety and delivering high-quality care.
What are the best strategies for resolving conflicts in interdisciplinary healthcare teams?
Resolving conflicts in healthcare teams that bring together diverse disciplines requires a focus on clear communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making. It’s crucial to build an environment of psychological safety, where everyone feels free to voice concerns or ideas without fear of judgment. This kind of openness lays the groundwork for addressing disagreements in a constructive way.
One effective approach is emphasizing patient-centered decision-making. This helps align the team by keeping everyone’s focus on the shared goal – delivering the best care for the patient. Regular team meetings and structured communication practices can also help clear up misunderstandings before they grow into larger issues. Additionally, fostering strong interpersonal connections among team members can ease tensions and build trust.
When each team member’s role is understood and appreciated, collaboration becomes smoother. This shared understanding not only helps resolve conflicts but also ensures the team works together effectively to provide top-notch care.
Why is conflict resolution training essential for healthcare professionals?
Conflict resolution training plays a key role in helping healthcare professionals handle workplace disagreements constructively. This not only creates a more positive work environment but also directly impacts the quality of patient care. In the fast-paced world of healthcare, conflicts can stem from miscommunication, clashing expectations, or even personal differences. If ignored, these issues can disrupt team dynamics, compromise patient safety, and lower the overall standard of care.
With the right training, healthcare workers develop essential skills like clear communication, emotional awareness, and problem-solving. These tools enable them to address conflicts calmly and effectively, preventing situations from escalating. Beyond resolving disputes, this training strengthens teamwork and encourages professional development. When conflicts are managed proactively, healthcare teams can minimize errors, improve patient outcomes, and foster a workplace environment that supports both collaboration and high-quality care.