Getting certified as a Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA) is essential for career growth in healthcare. Employers value certifications, with 96% requiring or preferring them, and 70% offering higher pay to certified professionals. Certification options include the NHA (National Healthcareer Association), AAMA (American Association of Medical Assistants), AMT (American Medical Technologists), and NCCT (National Center for Competency Testing). Each has different eligibility criteria, exam formats, and renewal processes.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the key points:
- NHA (CCMA): Flexible eligibility (training or work experience), $160-$165 exam cost, 77% pass rate, requires renewal every 2 years with 10 CE credits.
- AAMA (CMA): Requires accredited program graduation, $125 exam cost, 76% pass rate, renewal every 5 years with 60 points.
- AMT (RMA): Requires 3–5 years of experience or education, $150 exam cost, 72% pass rate, renewal every 3 years with 30 points.
- NCCT (NCMA): Accepts 2 years of work experience, $119 exam cost, 53% pass rate, annual renewal with 14 CE hours.
Choosing the right certifying body depends on your education, experience, and career goals. NHA stands out for its flexibility, nationwide recognition, and focus on clinical skills like phlebotomy and EKG.
National Healthcareer Association (NHA) Overview
The National Healthcareer Association (NHA) is the largest certification agency for allied health professionals in the U.S. Since its founding in 1989, over 1 million healthcare workers have earned their certifications through NHA. The organization acts as a bridge between healthcare professionals, employers, and educators, highlighting the importance of certification in the industry.
One of NHA’s flagship certifications is the Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA). This credential, accredited by the National Commission for Certifying Agencies (NCCA), ensures that candidates meet national standards and are skilled in both clinical and administrative tasks.
Frank Preston, President and Director of Education, reflected on the impact of NHA certifications:
"The credentialing that NHA has allowed our students to have over the past 15 years has validated their skill set. It’s been a great partnership."
Data shows the strong demand for NHA certifications. Between 84% and 98% of employers require or encourage certification for allied health roles, and 51% believe newly certified CCMAs are fully prepared for their responsibilities. Schools that use NHA’s exam prep resources have reported a 90% improvement in pass rates and overall program outcomes.
How to Get Certified Through NHA
To earn the CCMA credential, candidates need a high school diploma or GED and must meet one of the following criteria: complete a medical assistant training program within the last five years, have one year of supervised medical assisting experience in the past three years, or accumulate two years of supervised experience within the last five years.
The certification process includes five steps:
- Create an NHA account and verify your eligibility online.
- Register for the exam – you’ll have six months to take it after registering.
- Prepare using NHA study tools, such as flashcards and practice tests.
- Take the exam, either at your school, a PSI testing center, or from home through Live Remote Proctoring.
- Receive your results, with electronic certificates available within two days.
The exam features 180 multiple-choice questions (150 scored and 30 unscored pretest items) and lasts three hours. A passing score is 390 on a 200–500 scale. In 2024, the exam had a passing rate of 81.38% from 78,681 test-takers. Clinical Patient Care makes up the largest portion of the test, accounting for 56% of the questions.
Costs for the exam range from $160 to $165, with optional study materials priced at $62–$69 for an online guide, $44–$49 for three practice tests, or $83–$94 for a bundle. If you fail, you must wait 30 days before retaking it; after three attempts, a one-year waiting period applies.
Once certified, CCMAs gain access to a wide range of career opportunities across healthcare settings.
Where NHA Certification is Accepted
NHA certifications are recognized nationwide, making them portable across different states. The organization collaborates with employers and educators to ensure its exams align with industry needs and job expectations.
Certified professionals can work in hospitals, outpatient clinics, long-term care facilities, pharmacies, and even insurance companies. Notably, 89% of healthcare organizations require or encourage certification for medical assistants. As Jordan Perry, a CPCT/A, put it:
"We’re going to be taking care of people’s lives. This certification proves that you’re capable of doing that."
Adding credentials to your resume can also set you apart in a competitive job market. With 35% of employers reporting that medical assistants are taking on more responsibilities than in previous years, having an NHA certification can give you an edge.
Renewal Requirements and Continuing Education
Renewing your NHA certification is simple. Credentials must be renewed every two years, requiring 10 continuing education (CE) credits and a recertification fee of $169 to $179. NHA offers free CE courses for current certification holders, making it easier to fulfill this requirement.
If your certification lapses for over a year, you’ll need to retake the full exam. Keeping your certification current is essential for career growth and avoids the extra time and cost of re-testing. The NHA also supports stacking credentials, like adding Phlebotomy or EKG certifications, to boost your qualifications.
Jessica Aponte, a CCMA, shared how her certification changed her life:
"My NHA certification has helped me financially advance my career. Most importantly it has given me opportunity to get a job that allows me to be a better mom by being home in the evenings and on the weekends."
sbb-itb-7a67ffa
NHA vs. Other CCMA Certifying Organizations
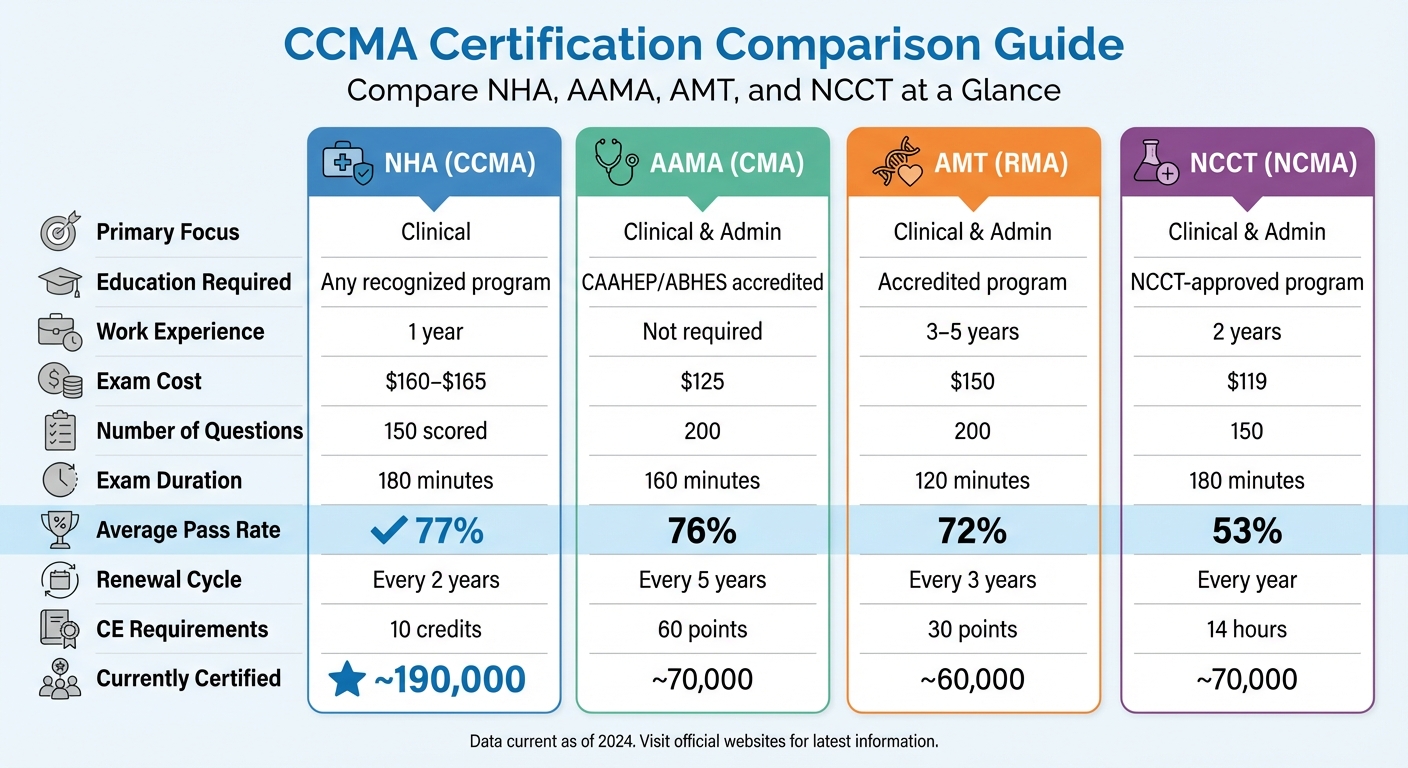
CCMA Certification Comparison: NHA vs AAMA vs AMT vs NCCT
Let’s break down how the National Healthcareer Association (NHA) stacks up against other major CCMA certifying organizations, such as the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA), American Medical Technologists (AMT), and the National Center for Competency Testing (NCCT). Each organization offers distinct pathways, exam structures, and renewal processes that can shape your certification journey.
Requirements and Exam Differences
Eligibility requirements differ across these organizations. NHA allows candidates who have completed recent training or have one year of supervised experience. AAMA, on the other hand, requires candidates to graduate from a CAAHEP/ABHES-accredited program. NCCT accepts candidates with two years of work experience, while AMT has the most stringent requirement, demanding three to five years of experience for those without formal education.
The exam content also varies. NHA’s CCMA exam places a strong emphasis on clinical skills, including phlebotomy, EKG, and infection control. Meanwhile, the AAMA (CMA) and AMT (RMA) exams balance clinical and administrative topics.
In terms of structure, the NHA exam includes 150 scored questions to be completed in 180 minutes. Comparatively, the AAMA and AMT exams include 200 questions, with durations of 160 and 120 minutes, respectively. Pass rates also vary: NHA leads with a 77% pass rate, followed by AAMA at 76%, AMT at 72%, and NCCT at 53%.
Cost and Access to Resources
The cost of certification exams ranges from $119 to $165, depending on the organization. NCCT offers the most affordable exam at $119, followed by AAMA at $125, AMT at $150, and NHA at $160–$165. Renewal fees are another consideration – NHA charges about $185 every two years, while AAMA’s fee is $65 every five years.
NHA offers several resources to support exam prep, including an interactive online study guide, practice tests, and a mobile app. They also provide free continuing education courses through a 24/7 online library. Another standout feature is NHA’s flexible testing options, allowing candidates to take the exam at their school, a PSI testing center, or even at home via Live Remote Proctoring. This flexibility is especially helpful for those juggling work and family responsibilities.
Side-by-Side Comparison Table
Here’s a quick comparison of the main features offered by each certifying organization:
| Feature | NHA (CCMA) | AAMA (CMA) | AMT (RMA) | NCCT (NCMA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Clinical | Clinical & Admin | Clinical & Admin | Clinical & Admin |
| Education Required | Any recognized program | CAAHEP/ABHES accredited | Accredited program | NCCT-approved program |
| Work Experience | 1 year | Not required | 3–5 years | 2 years |
| Exam Cost | $160–$165 | $125 | $150 | $119 |
| Number of Questions | 150 scored | 200 | 200 | 150 |
| Exam Duration | 180 minutes | 160 minutes | 120 minutes | 180 minutes |
| Average Pass Rate | 77% | 76% | 72% | 53% |
| Renewal Cycle | Every 2 years | Every 5 years | Every 3 years | Every year |
| CE Requirements | 10 credits | 60 points | 30 points | 14 hours |
| Currently Certified | ~190,000 | ~70,000 | ~60,000 | ~70,000 |
HealthCareer Certs is an excellent option for those preparing for NHA certification. Their program is 100% online, self-paced, and includes interactive tools, guaranteed externship placements, and one-on-one instructor support. Approved by the National Healthcareer Association, it also provides comprehensive resources to help you succeed on your first attempt.
How Certification Choice Affects Your Career
What Employers Look For
Certification isn’t just a nice-to-have – it’s often a must-have. In fact, 83% of employers list nationally recognized certifications as a critical hiring factor.
The specific certification you choose can make a big difference. Employers’ needs vary depending on the work environment. For example, the NHA CCMA certification is highly regarded for entry-level clinical roles because it focuses on practical skills like phlebotomy and EKG administration – tasks that outpatient clinics and specialty practices rely on daily. Another trend gaining traction is the preference for "stacked credentials." Employers increasingly favor candidates who hold multiple certifications, such as CCMA combined with Phlebotomy or EKG, to handle a wider range of responsibilities. Interestingly, 35% of employers have noted that medical assistants are taking on more responsibilities than ever before.
These preferences don’t just influence hiring – they also impact salaries and opportunities for career growth.
Salary and Advancement Opportunities
Earning a certification can significantly boost your paycheck. Certified healthcare workers in medical assistant roles earn, on average, 4.8% more per week than those without certification. Some reports suggest the pay difference can range from 15% to 25%. Beyond this, 70% of employers say they increase pay for employees who earn professional certifications.
The certifying body you choose also plays a role in shaping your career path. For instance, NHA’s recertification process is straightforward – requiring only 10 credits every two years – making it easier to keep your credential current while pursuing additional certifications or specialized roles. On average, medical assistants earn around $42,000 annually, with entry-level roles typically offering between $30,000 and $45,000. With the field projected to grow by 15% through 2033, maintaining an active certification is crucial for advancing into higher-paying roles, whether in specialized areas like cardiology or pediatrics or even in healthcare management.
NHA certifications also come with the advantage of nationwide recognition. They’re accepted by healthcare employers across all 50 states, giving you the flexibility to relocate without worrying about credential acceptance. In today’s job market, this kind of portability can be a game-changer, opening up opportunities in different regions and settings.
Choosing Your CCMA Certifying Body
Main Points to Remember
When deciding on a certifying organization, consider three key factors: your educational background, career aspirations, and the preferences of employers in your area.
First, check if your training program is accredited. If your school isn’t accredited by CAAHEP or ABHES, your best options are the NHA or NCCT, as the AAMA has stricter eligibility criteria. This flexibility allows certifications to align with different career paths and stages.
If you’re a recent graduate aiming to quickly step into a clinical role, the NHA CCMA certification might be the ideal choice. It emphasizes practical skills like phlebotomy and EKG administration – skills that are highly valued in outpatient clinics and specialty practices. Another advantage is the straightforward maintenance requirement: just 10 continuing education credits every two years, making it one of the easiest certifications to maintain.
For those with at least two years of experience as uncertified assistants, the NCCT NCMA offers a direct certification pathway without requiring additional training. However, it’s worth noting that this certification needs to be renewed annually, with 14 continuing education hours required each year.
Lastly, consult employers in your area. Regional preferences can play a significant role in your decision, as aligning with local employer expectations can improve your chances of landing a job and advancing in your career.
FAQs
How does the NHA compare to other CCMA certification organizations?
The National Healthcareer Association (NHA) has earned a reputation for its broad recognition and straightforward certification process. Founded in 1989, the NHA is a trusted name in healthcare certifications, including the Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA). Employers across the United States widely accept this certification, making it a popular option for those pursuing a career as a medical assistant.
While other organizations like the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) and American Medical Technologists (AMT) also provide certifications – such as the CMA and RMA – their eligibility requirements and certification names may differ. The NHA’s certification path typically involves completing an approved training program or gaining relevant work experience before sitting for the exam. The exam itself is designed to be both efficient and accessible.
The NHA’s strong reputation and nationwide acceptance often make it a top choice among employers. However, it’s essential to carefully review the requirements and benefits of various certifying bodies to find the option that best aligns with your career aspirations.
What makes NHA’s certification renewal process different from other organizations?
The NHA renewal process is designed to be straightforward and easy to navigate. To renew your certification, simply log into your NHA account, check your certification status, and ensure you complete 10 continuing education (CE) credits every two years. You can conveniently track your progress online. Plus, NHA offers online CE courses as part of its membership perks, which is a huge time-saver for busy professionals.
While other certifying organizations might have similar requirements, like earning CE credits and paying renewal fees, their processes can differ. Some may require in-person courses or additional steps. What sets NHA apart is its emphasis on online accessibility, streamlined processes, and ongoing professional support – making it a practical and user-friendly choice for keeping your credentials current.
Why do employers value NHA certifications for CCMA roles?
Employers place high importance on NHA certifications for Certified Clinical Medical Assistants (CCMAs) because they carry accreditation from the National Commission for Certifying Agencies (NCCA). This accreditation signifies that the certification adheres to rigorous standards and is widely acknowledged throughout the U.S. healthcare field.
Beyond accreditation, NHA certifications highlight a candidate’s dedication to their profession and validate their expertise. Healthcare organizations often rely on NHA-certified professionals, confident in their ability to provide skilled and dependable patient care.